Owning a dog is an amazing experience, with hundreds of lovely moments. Dogs are humans’ best friends, and they give us never-ending love and support.
The fact that dogs cannot live as long as humans do brings tears to the eyes. With hundreds of different kinds of dogs, there is no firm answer to how long the dogs live.
The Average Life Span of Dogs
According to studies, if your dog is unconditionally loved and well taken care of, it will have an average life span of 11-12 years. Several factors affect the life expectancy of your dog, such as:
● Breed: Dog breed plays the most important role in their life span. Purebred dogs are most likely to catch diseases and hence live for a shorter period. On the other hand, mix-breed dogs live longer due to a strong immune system.
● Weight: Smaller dogs have less weight and stay alive for a longer time than over-weight dogs. Dogs that weigh more have shorter life spans due to heart diseases.
● Nourishment: Dogs that have a diet with essential supplements are more likely to stay healthy and have a longer life.
● Health: Dogs with no health issues will definitely stay with you longer than those with serious health problems.
How Long Do Dogs Live With Cancer?
Finding out your dog has cancer can be really scary and makes you think how long do dogs live with cancer? Cancer is a deadly disease in which there is an abnormal growth of cells in the body. Like humans, dogs can have different types of cancers as well.
A dog diagnosed with cancer, getting chemotherapy, lives for an average of 12 months or more in some cases. However, if left untreated, it hardly has two months.
How Long Do Dogs Live With Heartworms?
It is a disease where small larvae form into mature worms in the heart, lungs, or dogs’ blood vessels. The bite of infected mosquitoes commonly causes it. Although the treatment for heartworms is a bit costly, 95% of the dogs get well if treated properly.
The lifespan of your dog is not affected much if it is treated. The average heartworm lives in the dog for six years, which means your dog has many years to get better.
How Long Do Dogs Live With Diabetes?
Diabetes is a long-lasting but highly manageable disease, whether in humans or dogs. It is caused by the inadequate release of insulin hormone or high glucose levels in the bloodstream.
The life span of your dog diagnosed with diabetes depends on a lot of things such as the will of the dog to take medications and the age of your dog. Dogs with diabetes can have a normal life span with proper treatment.
How Long Do Dogs Live With Kidney Failure?
Kidney failure is a chronic disease, where kidneys are unable to perform their role. They cannot separate the waste substances from the blood, which is the primary function of kidneys.
This question, “how long do dogs live with kidney failure?” has many answers. The satisfactory one is that your dog can live up to 4 years with standard treatment and follow-up.
Addison’s in Dogs

If your dog has been losing weight or vomiting a lot, take it to your vet immediately. There are chances that your dog has Addison’s disease. Addison’s in canines is an uncommon disease as only 0.28 % of canines get it. Among those who have this disease, young female dogs are a common target, but it can be diagnosed in any dog.
What is Addison’s disease for Dogs?
The scientific term for Addison’s disease is Hypoadrenocorticism, which is hormonal dysfunction. Humans and animals have adrenal glands located on their kidneys. Those adrenal glands are responsible for releasing different hormones, which are essential for life. In Addison’s disease, there is a decrease in the production of those adrenal hormones.
If left untreated, this disease can be fatal. Fortunately, because of the modern diagnosis and medicines, the role of Addison’s disease in dog’s life expectancy is very little.
How does a Dog get Addison’s disease?
If your dog has been diagnosed with Addison’s disease, you might want to know what caused it. Most of the time, the root cause is unknown, but according to veterinarians, it happens due to autoimmune dysfunction. Sometimes, tumors in the body destroy the adrenal glands. Destruction of those glands lowers the production of the necessary hormones, causing Addison’s disease for dogs.
For someone who still doesn’t understand how does a dog get Addison’s disease, it can also be due to trauma, loss, or infection. Dogs are likely to experience trauma if their owners abandon them or the death of the owner.
In some cases, Addison’s disease in dogs occurs from the treatment of Cushing’s disease. Cushing’s disease is a condition where too many adrenal hormones are being produced in the body. Medications to slow down the production of adrenal hormones sometimes excessively lower the hormone production and cause Addison’s disease.
What are the Symptoms of Addison’s in Canines?
There are several signs associated with this disease, which make it difficult to rule it out. For this feature, Addison’s disease is often known as the great imitator. The signs and symptoms of Addison’s disease are usually unclear. Common signs are:
- The dog has a low pulse
- You notice blood in your dog’s stool
- Your dog has diarrhea
- Dog is not eating properly
- Depression in dogs
- Your dog has become skinny for no reason
- Your dog is acting lazy and doesn’t want to play
- Vomiting
- You notice your dog is losing a lot of hair
- Increase urination
- Irregular heartbeats
How is Addison’s disease Diagnosed in Dogs?
Typically, veterinarians diagnose your dog based on previous medical reports and medication history. Some blood and urine exams are run by the vet, along with other tests like ACTH and ECG. ACTH test measures the cortisol levels in the blood. In some cases, Addison’s disease is not diagnosed until the dog collapses and enters a critical form of this disease.
How is Addison’s disease Treated?
In severe cases, the priority of the veterinarian is to hospitalize the dog and control the hormonal deficiency through therapy. For dogs that are not in an acute condition, a hormonal replacement medication is given. Addison’s disease cannot be cured completely, so your dog must take those medications for a lifetime. With time the dose is adjusted according to the health and lifestyle of your dog.
Addison’s disease dog’s treatment cost is somewhat around $700 to $1,500, depending on the overall diagnosis process and your vet fee.
How to Prevent Addison’s disease?
This disease is not something you can prevent. But it is better to have your dog checked if it shows any of the symptoms mentioned above. In this way, you can prevent it from getting into any kind of medical emergency.
Parvo In A Dogs
Dogs are lovable and loyal creatures. Every dog owner wants to see his/her dog enjoying good health. Just like us, dogs are also prone to several infectious diseases. Parvovirus infection is one of the major infectious diseases that cause several health complications in dogs.
Here, we will discuss some key signs and symptoms of parvovirus infection in dogs for better diagnosis and effective treatment.
WHAT IS CANINE PARVOVIRUS?
Canine parvovirus is an extremely contagious viral infection that affects dogs of all ages. But younger dogs/puppies are at higher risk. This infection can put your dog’s life in danger if not properly diagnosed and treated in early stages.
Susceptible dogs:
All dogs are susceptible to this infection, but the severe disease occurs in puppies between six weeks to six months. The following dog breeds are more vulnerable to contract parvovirus infection:
Mode of transmission:
This contagious virus can be transmitted and spreads from both direct and indirect routes.
Direct routes: Direct contact with an infected dog, direct contact with feces or mucus, so should read more about dog isolation to avoid outbreak the illnesses in the neighborhood or make their puppies at risk.
Indirect routes: Contact with infected equipment/utensils (feeding bowls, dishes, collars, leashes, toys, etc.), via personnel clothing (when a person touches an infected dog and then comes in contact with a healthy dog)
Note: This virus is resistant to cold, heat, and humidity, and drying. Additionally, it can survive in an indoor environment for one month (approx) and in an outdoor setting for many months.
Clinical manifestations (Early signs of parvo in a dog):
Dogs show various signs and symptoms depending upon the severity of the disease and should veterinarian confirm them, age, and immune state of the dog. Some critical signs and symptoms enlisted below:
- Loss of appetite (Anorexia)
- Dullness and depression
- Weightloss
- Increased body temperature (fever)
- Bloody diarrhea (dehydration due to excessive water and electrolytes loss)
- Vomiting and general body weakness (lethargy)
Note: Talk to your vet if you observe any of the above-given symptoms in your dog. Remember, dehydration, nausea, intestinal damage, and immune system damage can put your dog in septic shock.
What are the symptoms of parvo in puppies (Diagnosis and Treatment):
Your vet can diagnose the infection based on clinical signs and symptoms, history, blood and fecal (Stool) laboratory tests, and thorough physical examination.
Moreover, treatment includes the boost of the immune system supporting medications, fluid therapy (to replenish the lost electrolytes and fluid), and symptomatic medications to treat vomiting and severe diarrhea. In addition to that, early diagnosis and treatment give better outcomes. Otherwise, death occurs in 48-72 hours after the onset of clinical signs and symptoms.
Should not prescribe antibiotics to treat as it is not a bacterial infection
Prevention:
Parvovirus infection is highly contagious and spreads quickly from infected dogs to healthy dogs. It is better to quarantine (isolate) infected dogs from healthy ones. Give proper attention to infected dogs and feed an immune-boosting diet and medications (as suggested by your vet).
The best way to avoid parvovirus is to maintain the immunity of the dogs and puppies and keep your dog is up to date on vaccinations to prevent millions of viruses bacterial-infections. the unvaccinated dogs are more exposure to viral disease and distemper
Note: Dogs start shedding virus 4-5 days after getting exposed and continue shedding it till ten days after recovery.
Vaccination plays a vital role in preventing your beloved puppies from deadly parvovirus. Being a responsible owner, this is your duty to get your puppy vaccinated against the parvovirus (Directed by your vet).
QUICK OVERVIEW
- Name of the disease: Canine parvovirus
- Susceptible host: Dogs of all age
- Nature of the disease: Contagious
- Vaccination: Yes
- Zoonotic importance: No
- Prognosis Good: if diagnosed early.
Lyme Disease in Dogs
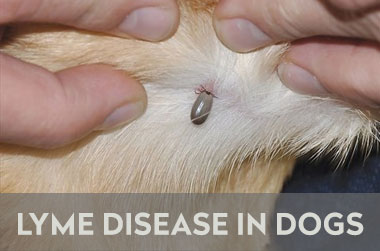
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a disease transmitted by tick bites and is caused by a spirochete known as Borrelia Burgdorferi.
It is challenging to detect Lyme disease in dogs. Once the bacteria enter the dog’s body, it can cause some serious problems and even lead to the death of the dog.
If you want to learn more about Lyme diseases in dogs, its signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, then read this article to the end.
Transmission of Lyme disease
The common tick that transmits Lyme disease is called a black-legged tick, also known as a deer tick. The deer tick is found throughout Europe, as well as in Canada and other countries.
The deer ticks habitat is primarily around wooded areas and most commonly around the ocean, rivers, and lakes. Deer ticks mainly bite animals during outdoor activities such as playing in the park or camping.
Lyme disease in dogs signs and symptoms
It is very difficult to detect Lyme disease in dogs signs and symptoms than in humans. The characteristic sign of Lyme disease in dogs bullseye rash does not form in dogs. In humans, this bull’s-eye rash appears three to 30 days after the bite of the infected tick.
However, other common signs that appear in dogs are like they are walking on eggshells, and often, most dogs feel pain in the body and stop eating.
Similarly, dogs with Lyme disease have pyrexia, joint pain, and often begin to limp. These symptoms in dogs appear immediately after the onset of Lyme disease, and joint pain can transfer from one leg to the other. These signs are often seen to disappear, and after a few days or weeks, they reappear.
Some dogs remain infected with Lyme disease for months or years, but no signs appear for that long. Eventually, when signs begin to appear, the disease may have spread throughout the dog’s body.
Common signs in whole-body infections are anorexia, vomiting, lethargy, kidney failure, and weight loss. The disease condition in which the kidney is affected is very rare, but if it appears, it can cause the death of your dog.
In some conditions of Lyme disease in dogs neurological symptoms appear after a tick bite. Symptoms found in dogs are persistent seizures, astasia, and hyperreflexia.
Diagnosis
Normally, when taking a dog with a limp, joints, and fever to the vet, they will diagnose it as Lyme disease. However, these are not clear signs of Lyme disease; certain blood tests will diagnose this disease. One blood test that is easy to perform in the clinic is the antibody test. Antibodies are usually formed as a result of a bacterial infection.
We use the tests to diagnose Lyme disease in dogs: joint fluid analysis, PCR (polymerase chain reaction), ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), and perform different bacterial culture tests to check the sensitivity of the disease. A complete blood test and urinalysis may also preform to assess the condition of the kidney.
Can you cure Lyme disease in dogs?
Lyme disease in dogs can be cured, and antibiotics are used for treatment for at least 30 days. This treatment plan often resolves the Lyme disease symptom, but if you didn’t treat the infection during this time, antibiotics might use for a long time. Certain therapies are also used with medications to relieve the symptoms of Lyme disease.
Lyme disease in dogs treatment cost
In recent years the cost of treating all diseases of dogs has increased. The cost of the antibiotic also doubles. A two-week course of antibiotics can cost you $ 400 in some areas. Similarly, lab tests can cost around $ 80 as well. However, this cost mostly depends on the type of test method used.
In dogs, Lyme disease can be very complicated, but you can protect your puppy by vaccinating him and giving him the right treatment.
Heart Murmur in Dogs

The idea of your dog having a heart-related disorder can be really terrifying for you. However, the important part is to know that heart murmur in dogs is not the disease itself but an indicator of underlying problems. They can minor to chronic illnesses. In dogs around the age of 5-years, 60% of them are affected by heart murmurs.
What is a Heart Murmur in Dogs?
You took your dog to the vet, and while listening to its heartbeat through a stethoscope, the vet noticed some irregularities. Those irregular heartbeats are known as heart murmurs in dogs. The heart’s normal rhythm sounds like lub-dub, but in heart murmurs, the rhythm is somewhat like a swoosh sound.
What is the grading of Heart Murmurs in Dogs?
The heart murmurs in dogs vary significantly based on their intensity, loudness, and location, which is why they don’t sound the same in every diagnosed dog. A greater level of intensity of heart murmur in dogs does not necessarily indicate severe heart disease.
Veterinarians have graded the intensity level of heart murmurs in dogs:
- Grade I: A stethoscope can hardly sense them.
- Grade II: Soft enough to be detected by a stethoscope.
- Grade III: Audible murmurs due to irregular blood flow.
- Grade IV: Loud enough to be detected from both sides of the chest.
- Grade V: Murmurs felt by placing a hand on the dog’s chest.
- Grade VI: Most audible and severe.
What Should A Dog’s Heart Rate Be?
When you get the answer to what is a heart murmur in dogs, you start focusing more on your dog’s normal heartbeats. Many people don’t know what should a dog’s heart rate be. The answer is that the normal heart rate for adult dogs is 60-100 beats per minute. This rate varies with the age of your dog; for new-born puppies, it is 160-200 beats/minute. For small dogs, the resting heart rate is around 100-140 beats per minute.
How bad is a Heart Murmur in Dogs?
This question is best answered by knowing the cause of heart murmurs in your dog. A variety of reasons can cause heart murmurs in dogs. The common one is due to irregular blood circulations within the heart. The abnormal flow of blood produces the sound heard through the stethoscope.
Some heart murmurs are because of structural problems in the heart, while others might not be due to heart diseases. Disorders of valves of the heart, blood vessels become narrow or wide, and a hole in the heart falls under structural heart diseases.
How to Treat Heart Murmur in Dogs?
If your dog has heart murmurs, its treatment depends on the type of heart murmur it has. The vets do not treat the murmurs but the underlying diseases linked with them. They are classified into two kinds concerning diagnosis. One is a physiologic murmur, which has no harmful impact on your dog. Physiologic murmurs do not need any treatment, but vets advise to monitor the dog from time to time. Due to their harmless nature, they are widely known as innocent murmurs.
On the other hand, pathologic murmurs need immediate attention and treatment as underlying diseases cause them. In such cases, specialized treatment plans are carried out by the vet. Your dog has to go through a series of medical procedures if the condition is severe. Some heart diseases even require surgical correction, along with medications. It is possible that your dog may need medical attention for years. If left untreated, heart failure is developed, which is fatal.




